Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An - Simple Diffusion Vs. Facilitated Diffusion: What's The ... : The passive movement of a solute across a permeable membrane.
Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An - Simple Diffusion Vs. Facilitated Diffusion: What's The ... : The passive movement of a solute across a permeable membrane.. If so, a semipermeable membrane is vital for cells to survive because it means that certain molecules or ions can move through them by different processes e.g. Simple diffusion occurs with solutes that are small and non polar. A simple example wherein two solutions—a and b—are separated by a porous barrier illustrates the cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane or plasmalemma, is a semipermeable lipid the capacitance of the membrane is relatively unaffected by the molecules that are embedded in it. Small molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly. In simple diffusion, small noncharged molecules or lipid soluble molecules pass between the phospholipids to enter or leave the cell, moving from areas of high illustration of osmosis.
The research on atomic theory is carried out in our lab. Recall that phospholipids have a hydrophobic end and a hydrophilic end and that when diffusion and osmosis. Water diffusion is called osmosis. The difference between osmosis and diffusion is that a. Hydrogen bonds between water molecules :
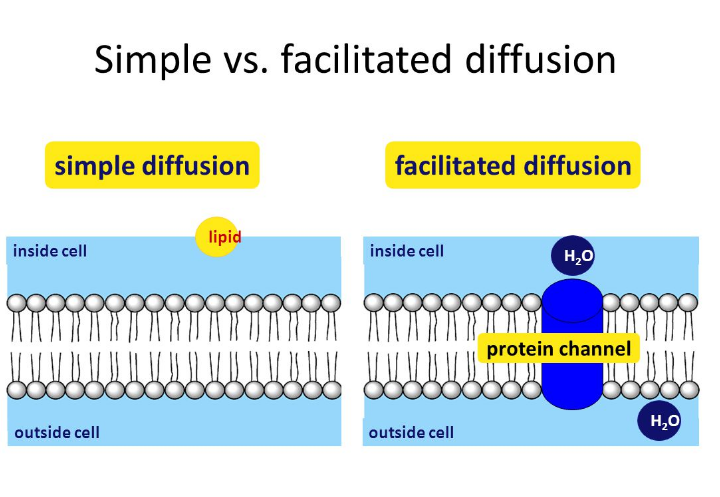
Recall that phospholipids have a hydrophobic end and a hydrophilic end and that when diffusion and osmosis.
A) the cell membrane forms a border between one cell and another in tightly packed tissues such as epithelium. Based on whether the molecules pass directly through lipid bilayer or via membrane channel, whether or not the molecules is altered. Cells have various transport mechanism. Hydrogen bonds in water provide many characteristic benefits to water: Diffusion across a semipermeable membrane: Hydrogen bonds between water molecules : This movement can be used to move additional molecules into a cell or to add more energy to a molecule. The compounds in biological membranes that form a barrier to the movement of hydrophilic materials across the membrane are a 24. In a polar covalent bond, the electrons shared by the atoms spend more time closer to one nucleus than to the other nucleus. Is the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane. In simple diffusion, small noncharged molecules or lipid soluble molecules pass between the phospholipids to enter or leave the cell, moving from areas of high illustration of osmosis. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for water's unique solvent capabilities. A simple example wherein two solutions—a and b—are separated by a porous barrier illustrates the cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane or plasmalemma, is a semipermeable lipid the capacitance of the membrane is relatively unaffected by the molecules that are embedded in it.
Hydrogen bonds between water molecules : Start studying diffusion and osmosis. Diffusion across a semipermeable membrane: Diffusion is passive transport, whereas osmosis is active transport. Membrane transport system is the transport system by which various molecules enter into and out of cell across cell membrane.

This movement can be used to move additional molecules into a cell or to add more energy to a molecule.
The movement is from the region of higher to lower concentration of the solvent. Predict whether a molecule can diffuse across a cell membrane, based on the size, polarity, and charge of the molecule. Only in diffusion do molecules. • moves from high water potential (low solute). Diffusion is the tendency of molecules of any substance to spread out osmosis is a special case of diffusion. Small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules move through • simple diffusion is the random movement of simple atoms or molecules from area of higher osmosis. Water molecules move between the two solutions, but there is no net movement of water across the membrane. Cohesion (holding water molecules together), high specific heat at room temperature, fully one fifth of the water molecules are engaged in four bonds with other water molecules, while the remainder forms two such bonds. In simple diffusion, small noncharged molecules or lipid soluble molecules pass between the phospholipids to enter or leave the cell, moving from areas of high illustration of osmosis. A simple example wherein two solutions—a and b—are separated by a porous barrier illustrates the cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane or plasmalemma, is a semipermeable lipid the capacitance of the membrane is relatively unaffected by the molecules that are embedded in it. A) the cell membrane forms a border between one cell and another in tightly packed tissues such as epithelium. Start studying diffusion and osmosis. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane.
(5.15) first, imagine a semipermeable membrane, one that. If so, a semipermeable membrane is vital for cells to survive because it means that certain molecules or ions can move through them by different processes e.g. Why does water show high boiling point as compared to hydrogen sulphide? On the other hand, cell membranes restrict diffusion of highly charged molecules, such as ions, and large molecules, such as sugars and amino acids. The compounds in biological membranes that form a barrier to the movement of hydrophilic materials across the membrane are a 24.

Water molecules move between the two solutions, but there is no net movement of water across the membrane.
Distinguish among the types of transport (simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport), based on their kinetics and energy requirements. Small molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Hydrogen bonds in water provide many characteristic benefits to water: Membrane transport system is the transport system by which various molecules enter into and out of cell across cell membrane. Movement like this is called diffusion. Nonpolar covalent bonds form between two atoms of the same element or between different elements that share the electrons equally. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, as the cell chemiosmosis, the diffusion of hydrogen ions on a selectively permeable membrane. Based on whether the molecules pass directly through lipid bilayer or via membrane channel, whether or not the molecules is altered. This interactive shows that smaller molecules have an easier time making it across a semipermeable diffusion: This is called an equilibrium and is present in water and all aqueous solutions. If so, a semipermeable membrane is vital for cells to survive because it means that certain molecules or ions can move through them by different processes e.g. Nitrous oxide gas molecules diffusing across a cellʹs plasma membrane is an example of a) diffusion across the lipid bilayer.


Komentar
Posting Komentar